

Postural Restoration Therapy (PRT) addresses asymmetrical patterns in the body by focusing on restoring proper alignment and function through specific exercises and techniques. By targeting the underlying postural imbalances, PRT aims to retrain the body to achieve a more symmetrical and balanced state, reducing strain and tension on muscles and joints.
PRT can be beneficial for chronic pain related to postural imbalances by addressing the root cause of the pain. By correcting asymmetrical patterns and improving alignment, PRT can help alleviate the strain on muscles and joints that may be contributing to the pain. Through targeted exercises and interventions, PRT aims to improve overall posture and reduce pain over time.
According to the CDC, osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that affects more than 32.5 million adults in the US alone. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint but typically targets the hands, knees, neck and lower back. Once considered a “wear and tear” condition, we now know that this is a disease of the entire joint, including bone, cartilage, ligaments, fat, and the tissues lining the joint. The post Understanding Osteoarthritis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment appeared first on Salinas Physical Therapy.

Posted by on 2023-06-27
Breathing plays a crucial role in PRT as it is used to facilitate proper alignment and movement patterns. By focusing on diaphragmatic breathing and incorporating specific breathing techniques into exercises, PRT helps to optimize the function of the respiratory system and improve overall postural alignment. Proper breathing patterns can also help to reduce tension and promote relaxation in the body.

PRT differs from traditional physical therapy methods by its focus on addressing asymmetrical patterns and postural imbalances as the underlying cause of pain and dysfunction. While traditional physical therapy may focus on treating symptoms, PRT takes a holistic approach to address the root cause of issues by restoring proper alignment and function through specialized exercises and interventions.
PRT can improve athletic performance by addressing postural issues that may be limiting an individual's movement and function. By correcting asymmetries and improving alignment, PRT can help athletes move more efficiently, reduce the risk of injury, and optimize their overall performance. Through targeted exercises and interventions, PRT can help athletes achieve their full potential.
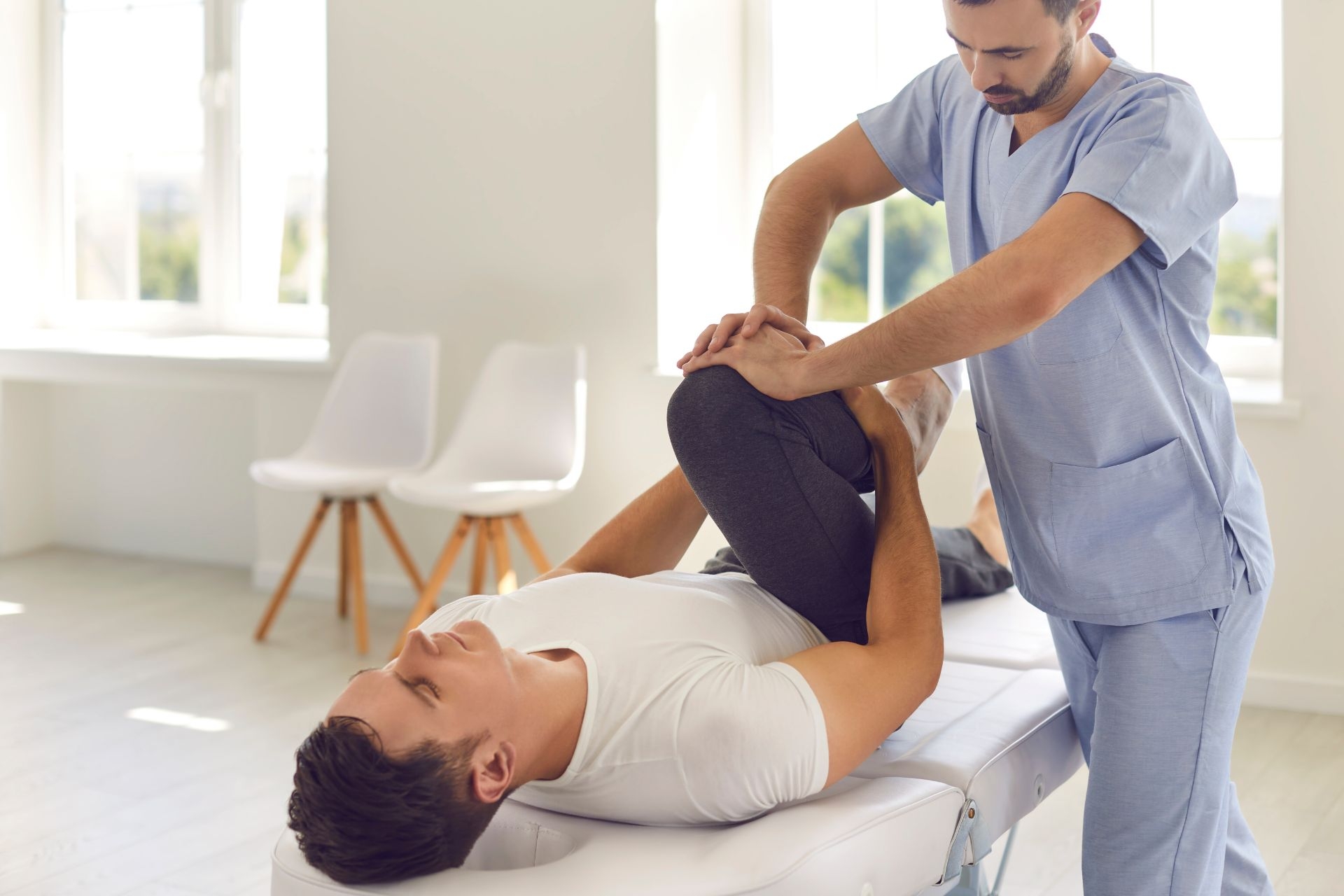
Specific exercises and techniques used in PRT to correct postural imbalances may include breathing exercises, muscle strengthening and lengthening exercises, postural repositioning techniques, and neuromuscular re-education. These exercises are designed to target specific areas of the body that may be contributing to asymmetrical patterns and postural imbalances, helping to restore proper alignment and function over time.
The time it takes to see results from PRT can vary depending on the individual's condition, severity of postural imbalances, and adherence to the treatment plan. Some individuals may experience improvements in pain and function within a few sessions, while others may require more time to see significant changes. Consistent practice of prescribed exercises and interventions is key to achieving lasting results with PRT.

Constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) complements traditional physical therapy for stroke survivors by focusing on intensive, repetitive practice of the affected limb while constraining the unaffected limb. This approach helps to promote neuroplasticity, improve motor function, and enhance overall functional abilities. CIMT also incorporates behavioral techniques to encourage the use of the affected limb in daily activities, leading to greater independence and quality of life for stroke survivors. By combining CIMT with traditional physical therapy, individuals can experience a more comprehensive and effective rehabilitation program that targets specific deficits and promotes long-term recovery.
Incorporating hydrotherapy, or water-based exercises, into a rehabilitation program offers numerous benefits for individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries. Hydrotherapy provides a low-impact environment that reduces stress on joints and muscles, making it ideal for those with limited mobility or chronic pain. The buoyancy of water supports the body, allowing for increased range of motion and flexibility during exercises. Additionally, the resistance of water helps to strengthen muscles and improve cardiovascular fitness. The warmth of the water can also help to relax muscles and reduce inflammation, promoting faster healing. Overall, hydrotherapy can enhance the effectiveness of a rehabilitation program by providing a safe and effective way to improve physical function and overall well-being.
Robotic-assisted therapy in neurorehabilitation settings has a wide range of applications that can benefit patients recovering from neurological injuries or conditions. These applications include motor learning, functional recovery, muscle strengthening, coordination improvement, gait training, balance training, and proprioceptive feedback. The use of robotic devices allows for precise control over movement patterns, intensity levels, and progression of exercises, leading to more targeted and effective therapy sessions. Additionally, the real-time feedback provided by these devices can help therapists monitor progress, adjust treatment plans, and optimize outcomes for each individual patient. Overall, robotic-assisted therapy offers a promising approach to enhancing rehabilitation outcomes in neurorehabilitation settings.
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy has been shown to accelerate bone healing and improve fracture management when used in conjunction with physical therapy. The application of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound helps stimulate osteoblast activity, promoting bone formation and remodeling. This therapy also enhances the production of growth factors and cytokines, which play a crucial role in the healing process. By incorporating low-intensity pulsed ultrasound into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, patients can experience faster recovery times, increased bone density, and improved functional outcomes. This combined approach allows for targeted and effective rehabilitation, leading to better overall patient outcomes in bone healing and fracture management.
Graston Technique and instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM) enhance traditional physical therapy interventions by providing targeted treatment to specific areas of the body through the use of specialized tools. These techniques help break down scar tissue, improve blood flow, and promote tissue healing, leading to faster recovery and improved range of motion. By incorporating Graston Technique and IASTM into traditional physical therapy sessions, therapists can address soft tissue restrictions more effectively, resulting in better outcomes for patients with musculoskeletal injuries or chronic pain. Additionally, these techniques can help reduce inflammation, alleviate muscle tightness, and enhance overall functional performance, making them valuable additions to a comprehensive rehabilitation program.
Neuromuscular reeducation for patients with movement disorders involves a variety of specific techniques aimed at improving motor control and coordination. Some common techniques include proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) exercises, which focus on stimulating proprioceptors to enhance muscle activation and coordination. Another technique is biofeedback, which provides real-time information on muscle activity to help patients learn how to better control their movements. Additionally, mirror therapy can be used to help improve motor planning and execution by providing visual feedback to the brain. These techniques, along with others such as task-specific training and functional electrical stimulation, are tailored to each patient's specific needs and goals in order to optimize their motor function and overall quality of life.